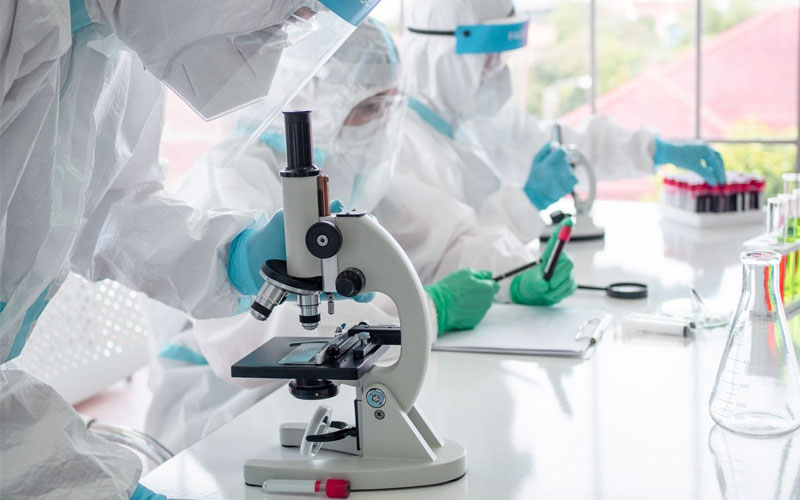
Laboratory construction process
Laboratory construction is a complex system engineering, which not only includes drainage, ventilation, power distribution, air conditioning, fire protection, waste gas, and liquid treatment, but also considers multiple factors such as environmental
Laboratory construction is a complex system engineering, which not only includes drainage, ventilation, power distribution, air conditioning, fire protection, waste gas, and liquid treatment, but also considers multiple factors such as environmental protection, safety, and sustainable development. So what is the process of laboratory construction?
1. Scientific planning scheme
The positioning and planning of the laboratory are the basis of the formal laboratory construction.
The laboratory planning scheme includes laboratory building planning and laboratory process planning, which requires a lot of preliminary research work.
It is necessary to clarify their own needs and the development of laboratories and to extensively inspect the laboratories that have been built by the contractor.
2. Selection of constructor
When choosing a constructor, you must strictly inspect its design, R&D, production, and construction capabilities and qualifications, inspect its completed projects and the location of the company on the spot, and select the nearest construction unit.
After the design drawings are completed, third-party agencies and authoritative experts are invited to conduct a detailed review to avoid unreasonable designs and major defects. In the construction project, the other party should be required to have a project manager with practical experience, which is conducive to progress control, resource allocation, communication, and coordination.
3. Layout design
Layout design refers to configuring space according to laboratory needs, optimizing the layout and placement of instruments and equipment, fully considering the flow of people and the direction of items, etc., to ensure subsequent designs such as water, electricity in combination with furniture.
4. Laboratory power distribution system
The requirements of laboratory instruments and equipment for circuits are relatively complex. Many instruments and equipment have special requirements for circuits. For the design of power distribution systems, not only the existing instruments and equipment, but also the development plan of the laboratory for several years must be considered, and fully consider the reservation of the power distribution system and future circuit maintenance and other issues.
In order to ensure a stable power supply, a dual-circuit design should be considered. The capacity of the uninterruptible power supply should meet the actual needs and ensure a certain range of expansion to meet future development needs.
5. Laboratory water supply and drainage system
The pipes of the laboratory drainage system should be resistant to acid and alkali corrosion and the melting of materials by organic reagents. PPR or other materials should be used.
Due to the complicated sewer pipes in large laboratories, necessary measures should be taken to avoid blockage and leakage of the pipes.
6. Laboratory ventilation system
The laboratory air supply and exhaust system are one of the largest and most influential systems in the entire laboratory design and construction process.
Among them, the noise, the number of air changes in the room, the differential pressure, and the gas residue in the fume hood are all issues worthy of attention.
In addition, the sample room and reagent room should also be equipped with ventilation and exhaust equipment to prevent the odor brought by the sample from contaminating the environment.
7. Selection of laboratory furniture
The selection of laboratory furniture mainly involves elements such as countertop material, cabinet structure and material, and color matching.
For example, the pretreatment room should use acid and alkali-resistant ceramic plate countertops, and the instrument room should use physical and chemical board countertops.
The structure of the cabinet is mainly divided into three types: steel-wood, aluminum-wood, and all-steel. The support of the test bench can be divided into C-shaped and back-shaped, which should be determined according to the needs of each unit. The layout, type, and quantity of counters in each room should also be fully considered. Side counters, central counters, high cabinets, and hanging cabinets should be properly matched to avoid inconvenience in future work.
In addition, there are some details that should also be considered, such as the reasonable configuration of computer bits to avoid the inconvenience of future use.