What is WHO GMP?
1. What is WHO GMP? What is GMP? GMP (or Good Manufacturing Practices) is a system ensuring products are manufactured and monitored according to quality standards. These quality standards are created by agencies authorizing and licensing the manufacture
1. What is WHO GMP?
What is GMP?
GMP (or Good Manufacturing Practices) is a system ensuring products are manufactured and monitored according to quality standards. These quality standards are created by agencies authorizing and licensing the manufacture of pharmaceutical products, food and beverage, cosmetics, dietary supplements, and so on.
Read more: What is GMP? - GMP in pharma industry
What is WHO GMP?
WHO GMP is Good Manufacturing Practices, formulated by World Health Organization. WHO GMP is the guideline that pharma manufacturers must meet in their medicine manufacturing process.
The first version of WHO GMP was developed in 1968. One year later, WHO GMP is recognized as an integral part of WHO Certification Scheme on the quality of pharmaceutical products in the market.
Nowadays, more than 100 countries have incorporated WHO GMP standards into their countries' laws.
2. WHO GMP guidelines
Followed are some WHO GMP guidelines for pharmaceutical manufacturers:
Personnel
Principle:
- Manufacturing processes rely on personnel
- There must be sufficient qualified personnel in the manufacture of medicines
- Individual responsibility must be specified and documented in job description.
Requirements:
- Sufficient qualified and experienced personnel is required
- There should be specific job description for every staff
- Personnel must abide by GMP principles and receive regular training
- There should be systems in place for disqualification of personnel from entry into cleanrooms
Key personnel:
- Key personnel include: Head of Production Department, Head of Quality Department and authorized person
- Key personnel is responsible for monitoring the activities of production and quality departments.
- Key personnel must have the required scientific qualifications and experience in practice as required by national regulations.
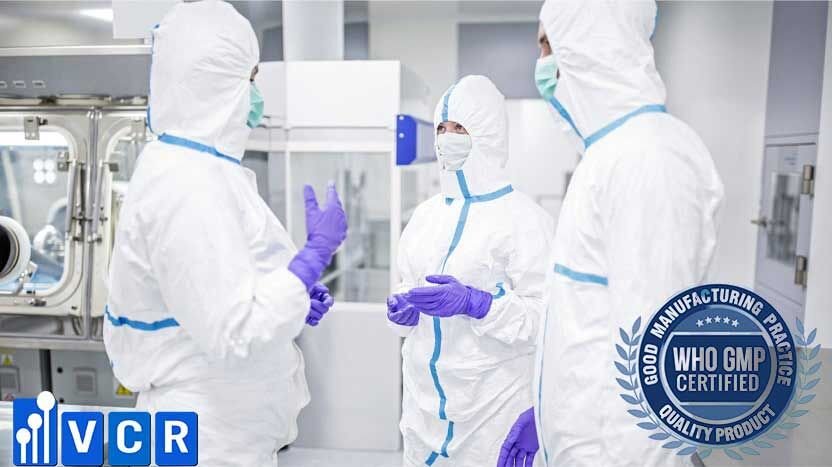

- The department heads share the responsibilities related to the quality of products.
- Each department head will have particular responsibilities.
- The training majors of personnel are as follows: Chemistry, chemical engineering, microbiology, science and technology in pharmacy, pharmacology and toxicology, physiology, and other related sciences.
WHO GMP personnel training:
- The manufacturer organizes training according to a written program for all employees in the manufacturing area.
- Newly recruited employees need to be trained in basic GMP principles and practice
- Intensive training is required for employees working in hazardous environments.
- Quality assurance issues should be thoroughly discussed in training courses.
- Visitors and untrained staff should not be allowed into the manufacturing and quality control areas.
Premises
Principle:
The premises should be located, designed, constructed, repaired, and maintained to suit the manufacturing operation.
Requirements:
- The premises design must aim to minimize the risk of errors and ensure hygiene and maintenance and avoid affecting cleanliness.
- Measures should be taken to avoid cross-contamination in dust-producing areas
- It should be placed in the right environment and protective measures to avoid contamination of the product
- It is necessary to design and build in accordance with the finished product factory to ensure good hygienic conditions.
- The factory needs to be carefully maintained, ensuring that this activity does not affect the product.

- Clean and disinfect manufacturing area if necessary
- Power, lighting, temperature, humidity, and ventilation must be adequate so as not to adversely affect the product and the operation of the equipment.
- Buildings should be designed and equipped to provide maximum protection from the entry of insects, birds or other animals.
- It is necessary to design the factory to ensure the reasonable movement of materials and employees.
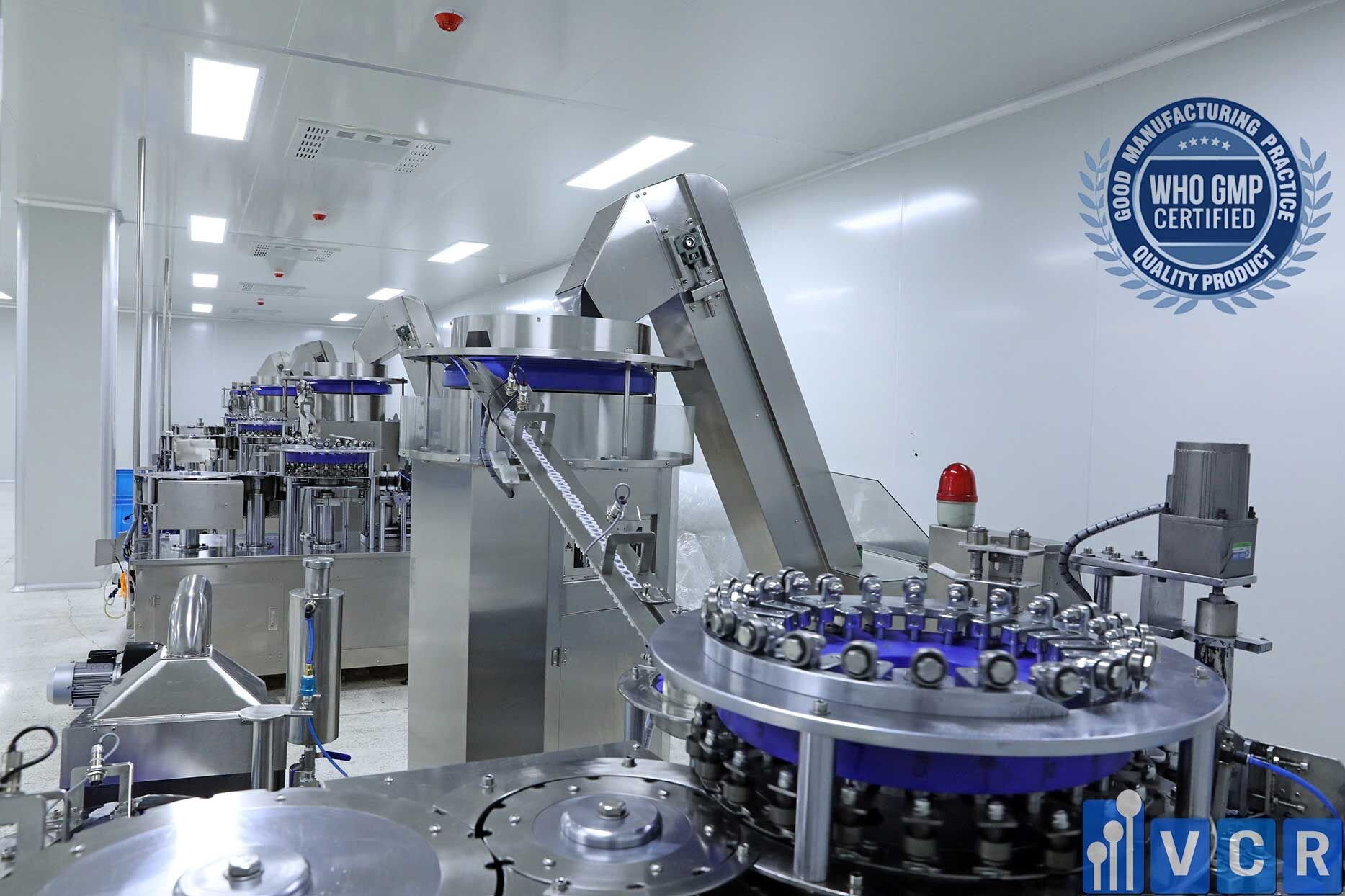
Device requirements
- Machinery and equipment must be arranged, designed, structured, adjusted, and maintained in accordance with the operations performed.
- Equipment should be installed to minimize errors and contamination
- Pipes should be clearly labeled indicating their contents and direction of flow if necessary.
- All pipes and equipment must be properly marked
- Scales and other suitable measuring equipment should be available for the production operation.
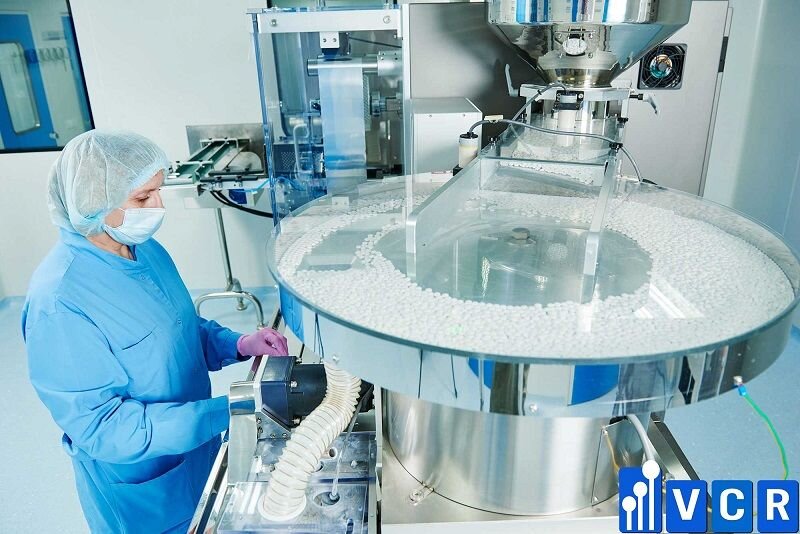

- Equipment needs to be cleaned according to a specific plan
- Laboratory equipment and instruments should be suitable for the test procedure.
- Select suitable auxiliary equipment to avoid becoming a source of contamination
- Machines and equipment must do harm to the product
- Damaged machines need to be taken out of the production area, checked, and repaired.
- Devices should be hermetically sealed
- Drawings of machines and equipment should be kept
Material
- No materials used for cleaning, equipment lubrication and insect control should come into direct contact with the product.
- Input materials and finished products must be quarantined until they are released for use or distribution.
- Both materials and products must be stored under suitable conditions specified by the manufacturer, that distinguish the lots and follow the first-by-first-out (FIFO) principle.
Hygiene control
Personal hygiene
- Employees need to receive medical check-up before and while being hired
- Staff need to be trained on personal hygiene practices
- Employees with obvious signs of ill health will not be allowed to participate in the product production process
- All employees should be instructed and encouraged to report conditions they believe may affect the product
- Operators avoid direct contact with raw materials, direct packaging materials, intermediates, and semi-finished products.
- Employees are required to wear clean clothing appropriate to the assigned work
- Smoking, eating, drinking, chewing, leaving plants, food, drinks, and personal smoking and medicines are not allowed in the areas.
- Staff need to have specific personal hygiene procedures.
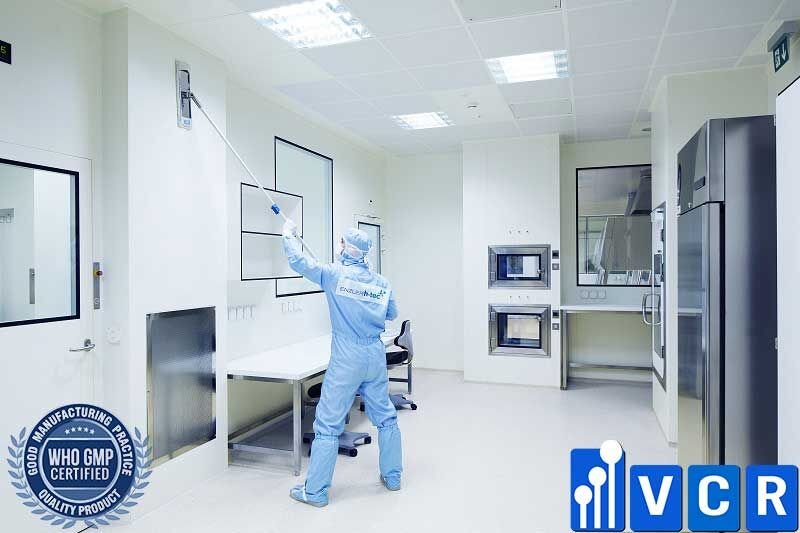
Factory cleaning
- The premises should be designed to be easy to clean.
- The floor is steep enough to drain all the water.
- The area for washing hands, changing clothes, and toilets should be located in an appropriate position
- Toilets are not directly connected to production and storage areas.

Documents
Requirements:
- Records should be carefully designed, drafted, reviewed, and distributed
- Appropriate authority person to approve, sign, and date is required
- Documentation must have clear content: clearly state the title and purpose of the record
- Documentation must be regularly reviewed and updated
- Documents need to be easy to read and indelible
- Any changes to a document must be signed and dated
- Record or complete records when conducting any activity
Basic Principles Profile in GMP WHO
All tutorials follow some basic principles as follows:
- The manufacture and distribution of medicines must minimize any risk to their quality.
- Manufacturing facilities must maintain a clean and hygienic production area, including laboratories and storage.
- Manufacturing facility design, operating principles, and environmental conditions must be controlled to prevent cross-contamination of medicinal products and to prevent cross-contamination from labeled or unlabelled materials or products.
- Manufacturing processes must be clearly defined, validated and controlled to ensure consistency and compliance with specifications.
- Any changes to the process are evaluated from the perspective of user safety and product quality, and any approved changes that could affect the quality of the drug are eligible.
- Instructions and procedures must be written in clear and unambiguous language.

- Operators should be trained to conduct production and control product according to approved and documented procedures.
- Records shall be made during production and quality control, demonstrating that all necessary steps required by defined procedures and instructions have been performed as defined and quality attributes product specifics have been met. Deviations must be investigated and recorded.
- The process must be maintained in a state of control throughout the product life cycle and improvements should be made as needed.
- Production records (including distribution) are kept in an easy-to-understand and accessible format, making it possible to track the complete history of a batch.
- A system must be in place to withdraw any lot from sale or supply.
- Complaints about marketed products should be reviewed, the cause of quality defects investigated, and appropriate measures taken for defective products and to prevent a recurrence.
WHO GMP guidelines are no regulatory guidelines for how products should be manufactured. They are a series of general principles that must be applied in the manufacturing process. When a company is establishing its pharmaceutical quality, manufacturing process and control systems, there can be many ways to meet GMP requirements. The company is responsible for determining the most efficient and effective quality process.
3. Benefits of WHO GMP
Benefits of WHO GMP to pharmaceutical companies
Despite many difficulties, if achieving GMP WHO certification, Vietnamese enterprises will have many advantages in the production and supply of drugs. The benefits that this standard can bring to businesses are:
- Prepare the quality management system for other certifications
- Increase competitiveness with pharmaceutical products from abroad
- Show commitment in producing and trading safe food to customers and consumers Increasing the trust and reputation of enterprises with customers and consumers, creating favorable conditions for enterprises to export drugs to difficult markets.
- Having a supporting effect when there is an assessment by competent authorities or related parties.
Benefits of WHO GMP to consumers
The benefits that GMP WHO brings to consumers can be mentioned as follows:
- The average consumer cannot detect whether a product, especially a drug, is good or not. WHO GMP will help them know this.
- The product manufacturing process follows strict regulations in each production step, ensuring the quality of the product meets the expectations of the consumer.
- Applying GMP helps consumers feel secure in choosing quality products.
- Help consumers have more confidence in the manufacturer.
- Improve public health, improve efficiency, and control food safety.
So we know what WHO GMP is? The core standards of WHO GMP together with the benefits that this set of standards bring to businesses and consumers. Hopefully, this article will help you better understand GMP and especially WHO GMP.
Read more: What is EU GMP?