EN 1822 standard - EPA, HEPA, and ULPA standard
The EN1822 standard is an important European filter inspection standard born in 1998 and is built to test and classify absolute filter.
- What is the European Standard EN 1822?
- Classification of Air Filters According to the EN 1822 Standard
- 3 Steps to Determine the Air Filtration Level According to the EN 1822 Standard
- How to Read the Filter Efficiency Parameters for EPA, HEPA, and ULPA Filters
- The Difference Between EN 779 and EN 1822 Standards
What is the European Standard EN 1822?
Classification of Air Filters According to the EN 1822 Standard
- Group E: EPA filtration (Efficient Particulate Air Filter) includes types E10, E11, and E12, which represent the efficiency levels that EPA filters must achieve.
- Group H: HEPA filters (High-Efficiency Particulate Air Filters) represent the efficiency levels that corresponding HEPA filters must achieve.
- Group U: ULPA filtration (Ultra-Low Penetration Air Filter) represents the efficiency levels that corresponding ULPA filters must achieve.
| Filter level | Total value (%)/MPPS | Local value (%)/MPPS | ||
| Filtering efficiency | Penetrating particles | Filtering efficiency | Penetrating particles | |
| E10 | ≥85 | ≤15 | - | |
| E11 | ≥95 | ≤5 | - | |
| E12 | ≥99,5 | ≤0,5 | - | |
| E13 | ≥99,95 | ≤0,05 | ≥99,75 | ≤0,25 |
| E14 | ≥99,995 | ≤0,005 | ≥99,975 | ≤0,025 |
| U15 | ≥99,9995 | ≤0,0005 | ≥99,9975 | ≤0,0025 |
| U16 | ≥99,99995 | ≤0,00005 | ≥99,99975 | ≤0,00025 |
| U17 | ≥99,999995 | ≤0,000005 | ≥99,999975 | ≤0,0001 |
The principle of filter inspection according to EN1822 standard
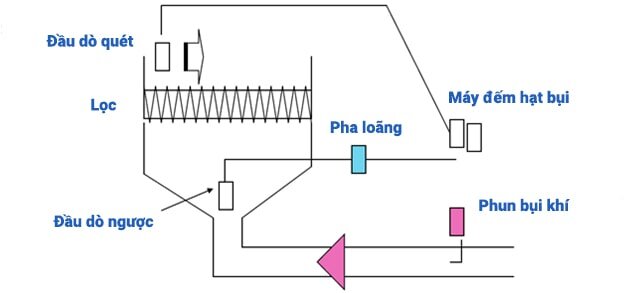
Test purpose
- Leakage check

- Overall performance
- Pressure loss
- Computer-made
- 6 particle counters (quickly and accurately detect leaks)
- Leak detection, pressure difference measurement, full performance
Report each filter of the scanner
- Filter model
- Filter serial number
- Actual pressure loss
- Actual MPPS performance
- Check for local leaks/intrusions
- Check the air flow
3 Steps to Determine the Air Filtration Level According to the EN 1822 Standard
- Step 1: A base gauge is used to determine the number and size of particles retained on the filter. After processing this data, the minimum particle size in the measuring medium is identified. This size is called the MPPS (Most Penetrating Particle Size).
- Step 2: Checking the leakage level of the filter element is an important test. This involves spraying an aerosol (a suspension of solid or liquid particles in air) along the surface of the filter plate using a probe. Data is collected to determine the integral value (overall efficiency) and the leakage rate across the filter surface.
- Step 3: The filtration performance of the filter plate is tested by measuring the pressure drop at the rated airflow rate. Using a set of measuring instruments and aerosol nozzles, the filtration efficiency for MPPS particles is then determined.
How to Read the Filter Efficiency Parameters for EPA, HEPA, and ULPA Filters
The Difference Between EN 779 and EN 1822 Standards
EN 779 Standard

| Group | Filter classification | End pressure | Average dust resistance level Am (%) | Average dust resistance level Am (%) | Minimum performance Em (%) |
| Pre Filter | G1 | 250 | 50≤Am≤65 | - | |
| G2 | 65≤Am≤80 | - | |||
| G3 | 90≤Am | - | |||
| G4 | - | - | |||
| Fine Filter | M5 | 450 | - | 40≤Am≤60 | - |
| M6 | - | 60≤Am≤80 | - |
EN 1822 Standard
| Filter level | Total value (%)/MPPS | Local value (%)/MPPS | ||
| Filtering efficiency | Penetrating particles | Filtering efficiency | Penetrating particles | |
| E10 | ≥85 | ≤15 | - | |
| E11 | ≥95 | ≤5 | - | |
| E12 | ≥99,5 | ≤0,5 | - | |
| E13 | ≥99,95 | ≤0,05 | ≥99,75 | ≤0,25 |
| E14 | ≥99,995 | ≤0,005 | ≥99,975 | ≤0,025 |
| U15 | ≥99,9995 | ≤0,0005 | ≥99,9975 | ≤0,0025 |
| U16 | ≥99,99995 | ≤0,00005 | ≥99,99975 | ≤0,00025 |
| U17 | ≥99,999995 | ≤0,000005 | ≥99,999975 | ≤0,0001 |