Laminar Airflow (LAF): Definition, Working Principle & Application
Did you know that nearly 9% of pharmaceutical products worldwide are contaminated due to airborne particles during manufacturing?
This statistic poses a significant challenge for pharmaceutical companies striving to ensure product quality and compliance with stringent GMP regulations. So what is the solution? The answer is Laminar Air Flow.
1. What is a laminar air flow system?
Laminar air flow (LAF), also known as laminar flow system, is a device that creates a clean, controlled environment. It effectively removes dust, bacteria, and other contaminants, allowing you to meet GMP standards and deliver pharmaceutical products of the highest quality and safety.
Laminar airflow systems create particle-free working environments by sucking air through a filtration system and exhausting it across a work surface in a laminar air stream. This laminar air stream, characterized by its smooth, unidirectional flow, ensures that contaminants are efficiently captured and carried away from the work area. They provide an excellent clean air environment for a number of cleanroom requirements.

2. Laminar airflow applications
The applications of laminar airflow systems are diverse in various sectors, including healthcare, pharmaceuticals, electronics, and research laboratories.
In pharmaceutical manufacturing, laminar airflow systems are crucial for creating and maintaining a sterile environment during the production of injectable drugs, protecting sensitive materials from contamination during research and development, and packaging sterile medical devices.
Laminar airflow systems also can be tailored to meet the specific requirements of different cleanrooms, such as varying sizes and configurations to accommodate different workflows and equipment.
3. Laminar air flow structure
Each component of an LAF system plays a crucial role in achieving optimal air filtration. The laminar flow system consists of 4 main parts: fan, pre-filter, DOP test ports, HEPA filter.
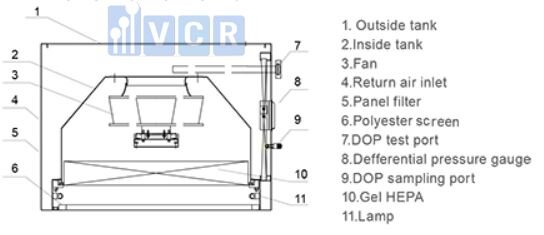
- Fan/Blower: A fan/blower is specially designed to draw air from the surrounding environment and create a continuous airflow within the LAF cabinet.
- Pre-filter: Acting as the first line of defense, the pre-filter removes larger particles like dust, hair, and fibers from the incoming air, extending the lifespan of the HEPA filter.
- HEPA filter: This is the heart of the LAF system. HEPA (High Efficiency Particulate Air) filters are composed of tightly woven fiberglass fibers capable of removing up to 99.97% of airborne particles as small as 0.3 micron, including bacteria, viruses, and mold spores.
- DOP test ports: These ports are used to test the efficiency of the HEPA filter using a DOP (Dispersed Oil Particulate) test machine. Regular testing ensures that the HEPA filter continues to operate at peak performance.
4. Advantages of laminar air flow systems for pharmaceutical production
High quality materials: Made of high-grade stainless steel, the seamless surfaces of LAF systems allow for easy cleaning and sterilization, preventing bacterial buildup.
High-efficiency filtration: The air within the LAF cabinet is constantly filtered through a HEPA filter held to the highest standards, ensuring that the air quality meets stringent GMP requirements.
User-friendly design:
- Built-in LED lighting offers bright, clear, and glare-free illumination for optimal operator visibility and comfort.
- A differential pressure gauge allows for continuous monitoring of the HEPA filter's performance, providing immediate alerts in case of any issues.
Reliable performance:
- The LAF system provides uniform airflow distribution throughout the work area, eliminating turbulent zones and dust accumulation.
- The positive pressure environment prevents contaminated air from entering the workspace, guaranteeing optimal product protection.
5. What is laminar air flow (LAF) working principle?
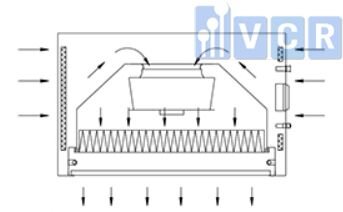
Laminar air flow unit works by the use of in-flow laminar air drawn through one or more HEPA filters, designed to create a particle-free working environment and provide product protection. Air is taken through a filtration system and then exhausted across the work surface as part of the laminar flows process.
Commonly, the filtration system comprises a pre-filter and a HEPA filter.
First, the air goes through the pre-filter (panel filter). Next, the fan blows the air towards the HEPA filter. HEPA filter captures the dust, bacteria, and airborne particles. Therefore, the HEPA filtered air is clean and particle-free.
6. Choosing the right laminar air flow systems for your needs
Based on the direction of airflow, laminar flow cabinets are categorized into two main types: Vertical Laminar Flow and Horizontal Laminar Flow.
Vertical Laminar Flow Unit
In this type of cabinet, clean air flows downward from the top of the LAF chamber onto the work surface and is exhausted through the base.
Vertical LAFs are often preferred for their enhanced operator protection, space-saving design, and ease of installation.
However, the downward airflow can be obstructed when working with taller objects.
Vertical LAFs are commonly found in applications requiring high levels of cleanliness and minimal equipment footprint, such as microbiology labs.
Horizontal Laminar Flow Unit
Unlike Vertical LAFs, airflow in a Horizontal LAF moves horizontally from the back of the cabinet towards the front, passing over the work area before being exhausted. This design offers a spacious work zone, making it suitable for handling larger items.
However, Horizontal LAFs require more floor space and provide less operator protection compared to Vertical LAFs. These cabinets are typically used in laboratories and production lines where ample workspace is necessary.

Video about laminar airflow
The choice between Vertical and Horizontal LAFs depends on various factors, including cleanroom space, operational needs, cleanliness requirements, and budget. Contact Vietnam Cleanroom today to receive expert advice on selecting the optimal laminar air flow solution for your specific requirements!
Kim VCR




















