What is cleanroom?
1. What is a cleanroom? Cleanroom is not just a room that is clean, but it has a special meaning and is defined by ISO standard as:
1. What is a cleanroom?
A cleanroom is not just a room that is clean, but it has a special meaning and is defined by ISO standard as:
"It is a room in which the concentration of airborne particles is controlled,
and is constructed and used in such a way to minimize the introduction, generation, and retention of airborne particles inside the room and in which other relevant parameters, e.g. pressure, temperature, and humidity are controlled as necessary."
The function of a cleanroom is to minimize the introduction, generation, and retention of particles, which is achieved by supplying large quantities of filtered air, personnel use clothing that minimize the dispersion of particles and the material used to build cleanroom does not generate any particle and can be easily cleaned.
A cleanroom can also control the temperature, humidity, sound, lighting, and vibration.

2. Cleanroom airflow patterns
Cleanrooms are classified into two major types based on their method of ventilation. These are
- Turbulent airflow cleanrooms
- Unidirectional airflow cleanrooms
Turbulent airflow cleanrooms are also known as "non-unidirectional". This type of airflow is generally used in offices, shops, etc. In this cleanroom, air is supplied by an air-conditioning plant through diffusers in the ceiling.
Unidirectional flow cleanrooms are also known as "laminar flow". The unidirectional cleanroom uses a large amount of air than the turbulent airflow cleanroom. Because of the directed air movement, it minimizes the spread of contamination about the room and sweeps it out through the floor.
(Image source: Spaceindustries UK)
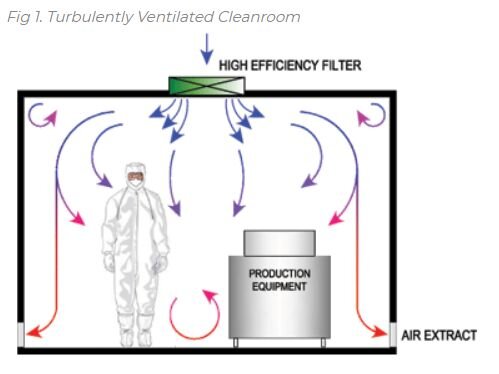
Fig.1 shows a turbulently ventilated cleanroom receiving clean air through air diffusers in the ceiling. Clean air mixes with the room air and removes airborne contamination by extracting the air at the bottom of the walls. The air changes are normally >20 per hour, this being much greater than that used in ordinary rooms. In this type of cleanroom, the contamination generated by people and machinery is mixed and diluted with the filtered air and then removed.
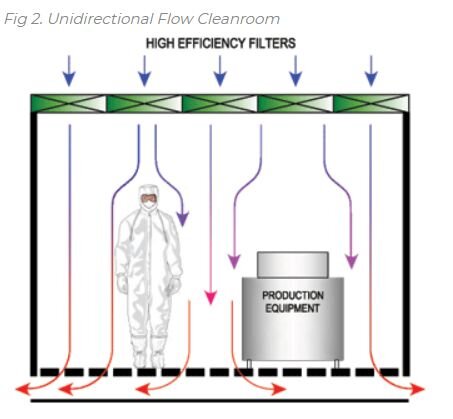
Fig 2. shows a unidirectional flow cleanroom. In this cleanroom, HEPA filters are installed across a ceiling and supply filtered air. The air sweeps all the contaminants from the room in a unidirectional way and exits through the floor.
3. Cleanroom Classification
Based on the application, cleanrooms are classified into:
- Industrial Cleanroom
- Biological Cleanroom
Biological cleanroom functions like industrial cleanroom. Besides, it also needs to control contamination and the density of micro-organisms.
Based on the cleanliness level, cleanrooms are classified according to:
- U.S Federal Standard
- ISO 14644
- EU GMP
U.S Federal Standard measured the class of cleanroom by the numbers of particles larger than 0.5 micron in diameter contained in one cubic foot of air. For example, Class 100 cleanroom contains fewer than 100 particles on one cubic foot.
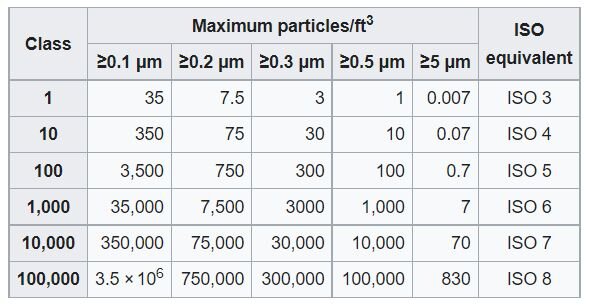
(Image source: Wikipedia)
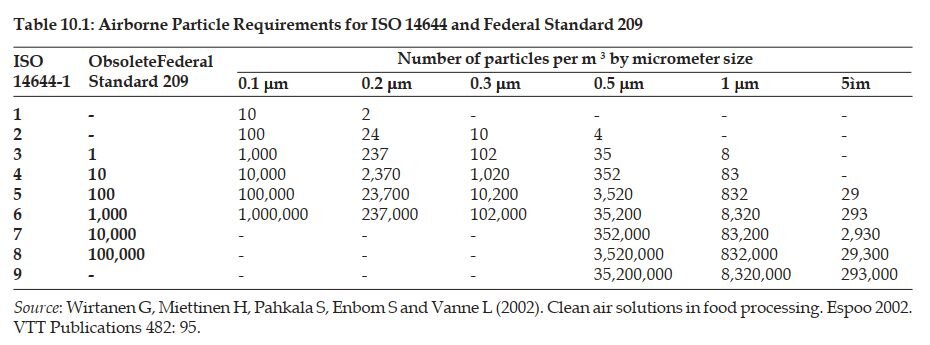
Beside U.S Federal Standard, ISO 14644 is another type of cleanroom classification.
ISO 14644-1 is a non-governmental standard developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
Table 10.1 shows the details of the two standards.
EU GMP is the guideline that pharmaceutical manufacturers must meet if they are intended for the EU market. EU GMP guidelines classify cleanrooms based on particles counts in operation and at rest.
In operation = during manufacturing process
At rest = when manufacturing process is finished
Class Maximum particles/m3 At rest In operation 0.5 μm 5 μm 0.5 μm 5 μm Class A cleanroom 3520 20 3520 20 Class B cleanroom 3520 29 352000 2900 Class C cleanroom 352000 2900 3520000 29000 Class D cleanroom 3520000 29000 Not defined Not defined
4. Negative and positive pressure cleanroom
Most of the cleanrooms are maintained at positive pressure. So if there is a leak, air leaks out of the room instead of unfiltered air coming in. These positive pressure rooms are usually applied in semiconductor and pharmaceutical manufacturing, where a tiny amount of airborne particles entering could contaminate the whole process.
Negative pressure cleanrooms are used in biology laboratories, handling hazardous organisms, or in operating theatres of hospitals. The poisonous viruses and particles are kept from escaping the room.
5. Contamination control in cleanroom
Cleanrooms are designed to minimize and control contamination. There are many sources of contamination. The atmosphere contains dust, microorganisms, condensates, and gases. The manufacturing process also produces a range of contaminants.
People are the greatest threat to cleanroom contamination. An average person sheds 1.000.000.000 skin cells per day.
In order to control the cleanroom contamination, practices are introduced as follows:
- The air entering a cleanroom is filtered to remove dust and particles, and the air inside is constantly re-circulated through HEPA filters. This is controlled through an HVAC system (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning)
- Staff enter and leave through airlocks and wear protective clothing such as hats, face masks, gloves, and boots.
- Equipment inside the cleanroom is designed to generate minimal air contamination. Cleanroom furniture is also designed to produce a low amount of particles and to be easy to clean.
- Cleanroom HVAC systems also control the humidity to low levels, such that extra precautions are necessary to prevent electrostatic discharges.
Vietnam Cleanroom Equipment (VCR) specializes in providing cleanroom equipment for construction contractors. We provide high-quality products with competitive prices and large quantities nationwide. The equipment includes:
Differential pressure gauge, FFU Fan Filter Unit, Pass box, Clean room air filter, HEPA box, Clean booth, cleanroom steel door, Isolator cabinet, and other equipment
For details, please refer to Vietnam cleanroom equipment official website