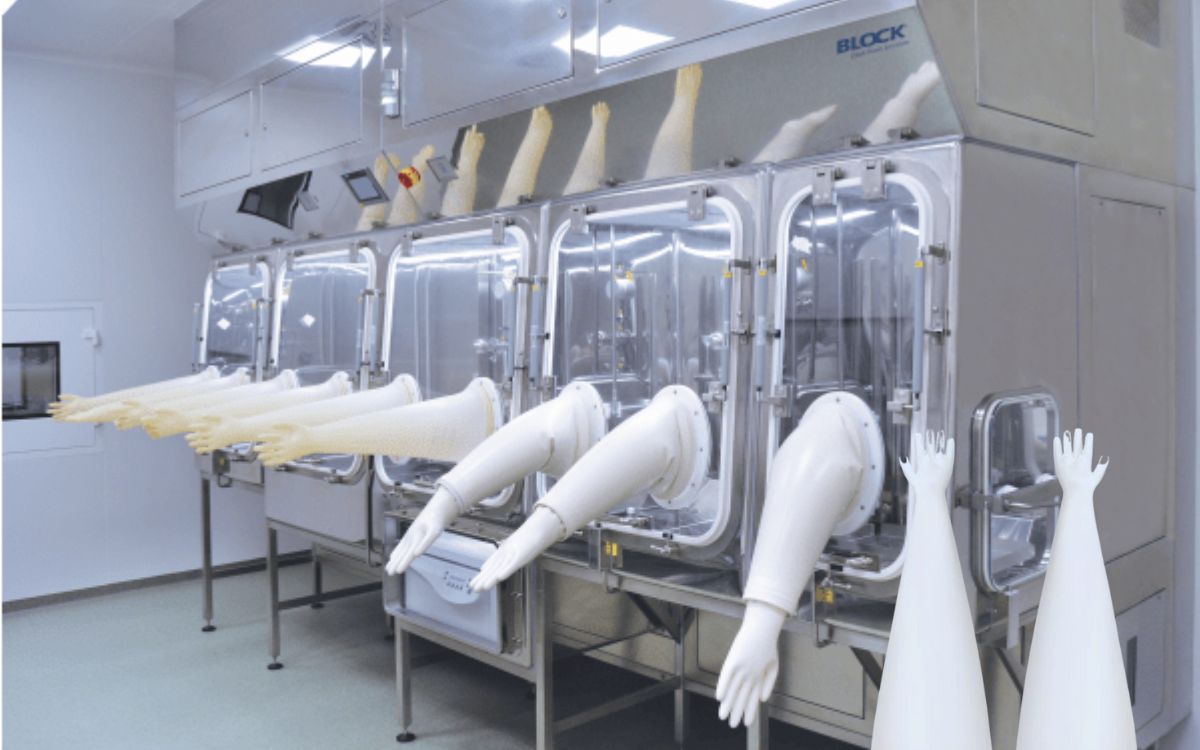
What are CSM gloves? Advantages and applications in pharmaceutical cleanrooms
CSM gloves are the premium choice in sterile areas of the pharmaceutical industry due to their strong chemical resistance, superior durability and suitability for isolators. As EU-GMP and WHO-GMP standards become increasingly stringent, CSM gloves become the optimal solution to protect compounding, filling and manufacturing processes for injectable
- 1. Overview of CSM (Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene Rubber)
- 2. Structure and Specifications of CSM Gloves
- 3. Outstanding Advantages of CSM Gloves in Pharmaceutical Environments
- 4. Quality Standards and Certifications for CSM Gloves
- 5. Applications of CSM Gloves in Pharmaceutical Cleanrooms
- 6. How to select CSM gloves correctly for each type of isolator
- 7. Maintenance, Cleaning & GMP‑Compliant Use
- 8. CSM - The Gold Standard for Isolator Gloves in Modern Pharmaceutical Manufacture
In the modern pharmaceutical environment, where every operation takes place under strictly sterile conditions, gloves are not merely protective equipment-they are the “shield” that ensures the safety of the entire production process. As EU-GMP and WHO-GMP standards continue to tighten, the demand for a glove material that offers strong chemical resistance, durability, and compatibility with isolators has become more urgent than ever. Among the many materials available, CSM (Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene Rubber) stands out as the premium choice, widely used in cleanrooms, compounding zones, aseptic filling areas, and injectable drug production lines. This article will help you understand what CSM gloves are, why this material is superior, and how to properly apply it in pharmaceutical settings to ensure safety, efficiency, and GMP compliance.
The pharmaceutical industry is entering an era where all standards related to safety, sterility, and risk control are being raised to unprecedented levels. EU-GMP, WHO-GMP, and PIC/S-compliant facilities must ensure that every operation in aseptic areas-particularly compounding, filling, syringe sealing, and handling of API/HPAPI-is conducted in fully controlled conditions. In this context, specialized gloves are not just personal protective equipment; they are integral components of isolator systems, directly impacting the safety, cleanliness, and process stability of pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Among materials such as nitrile, latex, neoprene, and butyl, CSM (Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene Rubber) emerges as the top-tier option today. Thanks to its strong chemical resistance, corrosion resistance, sterilization tolerance, low particulate shedding, and superior mechanical durability, CSM has become the preferred material in the production of injectables, vaccines, biologics, and other environments that require the highest levels of sterility.
This article will guide you through a comprehensive understanding of what CSM gloves are, the key properties of CSM material, the reasons behind its high evaluation, critical applications in pharmaceutical cleanrooms, along with essential standards, selection criteria, pricing references, and technical usage notes for GMP facilities. It is a complete reference for engineers, QA/QC professionals, procurement teams, and isolator operators alike.
1. Overview of CSM (Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene Rubber)
1.1 What is CSM? Origin and material characteristics
CSM (Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene Rubber) is a type of synthetic rubber created by sulfonating polyethylene (PE) polymers. Through a treatment process involving chlorine and SO₂, the molecular structure of polyethylene is modified, resulting in a material with exceptionally high chemical resistance and stability in harsh environments-surpassing what traditional rubbers can offer.
Key characteristics of CSM include:
- Superior chemical resistance: Resists degradation from strong acids, alkalis, and organic solvents-common in pharmaceutical and bioprocessing environments.
- Oxidation and ozone resistance: CSM does not age, crack, or become brittle under prolonged exposure to ozone or high-oxygen environments, which are typical in sterile zones.
- UV and radiation resistance: Maintains stability when exposed to UV light, making it suitable for environments with UV sterilization or high-intensity lighting.
- High elasticity and durability: CSM is flexible and elastic while maintaining mechanical strength, allowing gloves to perform reliably and durably inside isolators.
The combination of chemical resistance and flexibility makes CSM one of the most optimal materials for high-safety, strictly controlled applications.
1.2 Why is CSM chosen for the pharmaceutical industry?
In aseptic pharmaceutical production, glove materials must meet stringent requirements for cleanliness, durability, chemical resistance, and sterilization stability. CSM meets all these demands:
- Compatible with sterile environments and strong solvents: CSM gloves do not degrade when exposed to 70% IPA, ethanol, acetone, hydrogen peroxide, or other cleanroom disinfectants.
- Low particle generation - suitable for ISO Class 5-7: A critical GMP requirement is to limit particles released by gloves. CSM has a non-shedding structure that protects sterile environments within isolators.
- Resists discoloration and brittleness: Unlike many materials that fade or weaken after chemical exposure, CSM retains its integrity even after repeated sterilization.
- Suitable for routine sterilization protocols: Performs well under UV, VHP (vaporized hydrogen peroxide), IPA, or sterilizing gas exposure-essential for pharmaceutical compliance.
Thanks to these advantages, CSM has become the standard material for isolator gloves directly involved in injectable drug, vaccine, and high-potency API (HPAPI) production.
1.3 Comparing CSM to other glove materials
To highlight CSM's superiority, here's a comparison with common glove materials:
| Material | Chemical Resistance | Ozone/UV Resistance | Mechanical Strength | Comfort | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSM | Very High | Very High | High | Good | Isolators, pharmaceutical cleanrooms |
| NBR (Nitrile) | Medium-High | Medium | Medium | Good | Testing gloves, lower cleanroom classes |
| Neoprene | Good | Good | Medium | Good | Light to medium chemical handling |
| Butyl | Very High (esp. gases) | Good | Medium | Medium | Labs, hazardous chemical handling |
| Latex | Low-Medium | Low | Good | Excellent | Medical gloves, not suitable for strong chemicals |
2. Structure and Specifications of CSM Gloves
2.1 Three-layer design: contact layer - reinforced core - protective outer layer
CSM gloves are engineered with a specialized 3-layer construction, ensuring maximum chemical resistance while maintaining the flexibility needed for precise operations inside isolators.
- Inner Layer: Directly contacts the operator’s hand. Treated for optimal friction-anti-slip but smooth to the touch-allowing comfort during extended use.
- Reinforcement Core: The middle layer enhances tensile strength, tear resistance, and puncture protection. This gives CSM gloves the durability needed for intensive operations, which nitrile or latex gloves often cannot provide inside isolators.
- Outer Shield: The most critical layer for acid, alkali, and solvent resistance. Also protects against ozone, UV rays, and aging. Available in smooth or lightly textured finishes depending on the model.
Advantages of 3-layer construction:
- Maximized chemical resistance
- Maintains flexibility and does not stiffen with solvent exposure
- Ideal for precise handling in sterile environments
- Improves longevity and stability of gloves over time
2.2 Standard technical specifications
While different models exist, pharmaceutical-grade CSM gloves typically conform to these specifications:
Thickness: 0.4 mm - 0.8 mm
- 0.4 mm: For delicate handling, testing
- 0.6 mm: General use, multipurpose
- 0.8 mm: Strong chemicals, HPAPI
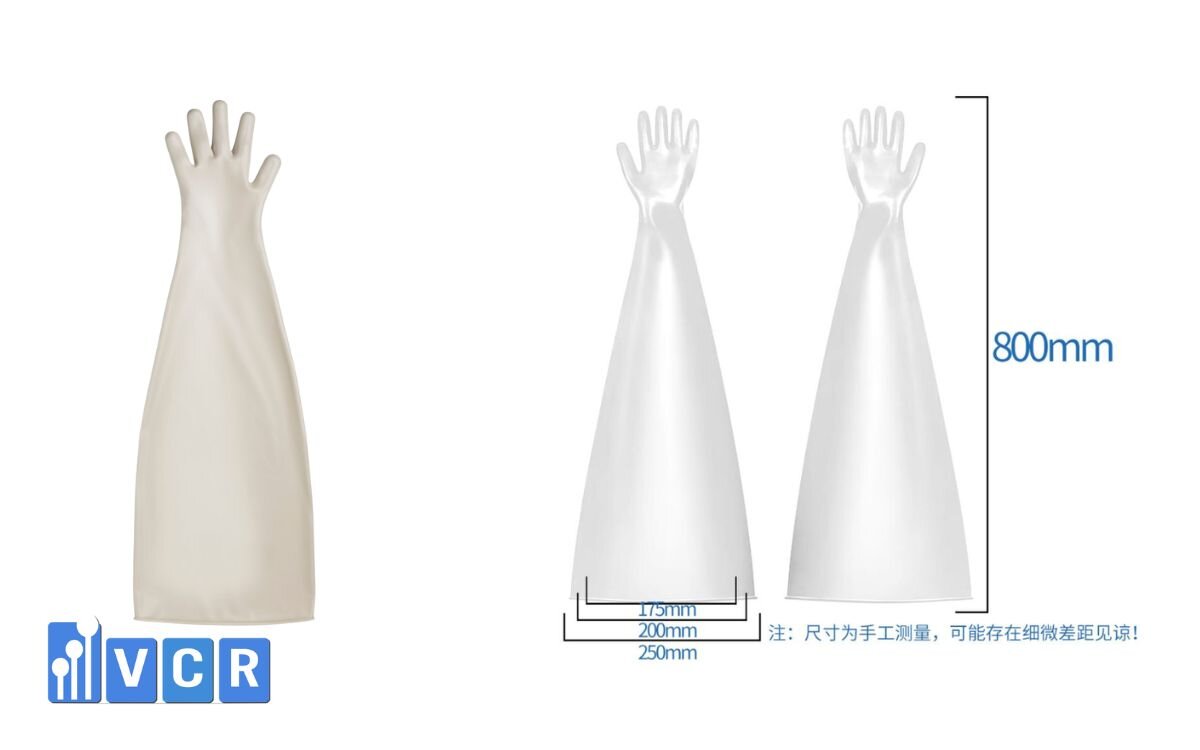
Length: 600 mm - 800 mm
Suitable for isolator ports (190 mm / 230 mm / 300 mm)
Color: Gray or black
Optimized for scratch detection, surface changes, or wear
Tensile Strength & Elongation:
Higher than NBR or neoprene, enabling comfortable manipulation
Abrasion Resistance:
High performance per EN 388 standards-reduces puncture or tear risk
Weight:
Depends on thickness, but heavier than NBR to enhance chemical durability
These parameters ensure that CSM gloves fully meet the operational demands of GMP-certified pharmaceutical facilities.
2.3 Common CSM glove models in the market
The current market offers several widely used CSM glove models for pharmaceutical isolators:
- CSM 404: Standard thickness, suitable for most compounding and testing zones
- CSM 602: Thicker and more durable, ideal for handling strong chemicals or heavy-duty operations
- CSM 800 mm long (for HPAPI isolators): Designed for high-toxicity compound handling with extended arm protection
- Seamless CSM gloves: Premium models without weld lines, reducing tear risk, improving airtightness, and ideal for high-level EU-GMP environments.
3. Outstanding Advantages of CSM Gloves in Pharmaceutical Environments
CSM gloves are considered the premium standard in the pharmaceutical industry due to their ability to simultaneously meet three key factors: safety, durability, and stability in sterile conditions. The following advantages explain why CSM has become the top choice for isolators and aseptic manufacturing areas for injectable drugs, vaccines, and biologics.
3.1 Top-tier Chemical Resistance
One of the primary reasons pharmaceutical facilities prioritize CSM is its superior chemical resistance, among the highest of all specialty glove materials:
- Resistant to strong acids: H₂SO₄, HCl, HNO₃ at high concentrations
- Resistant to organic solvents: IPA, ethanol, acetone, toluene
- Resistant to strong alkalis: NaOH, KOH, and alkaline buffers
CSM gloves are corrosion-resistant even under prolonged chemical exposure, especially in environments with regular cleaning or toxic substance handling (HPAPI). Unlike nitrile and latex, CSM maintains its physical integrity (no swelling, no brittleness) even during long-term contact.
3.2 High Mechanical Strength - Tear and Puncture Resistant
The mechanical durability of CSM is validated by EN 388 standard tests:
- Abrasion resistance: Level 4 (highest) - withstands repetitive movement and intensive tasks in isolators
- Tear resistance: Level 1 - ensures gloves don’t rip during stretching or minor impacts
- Puncture resistance: Level 1 - protects operators from accidental contact with sharp edges
Due to this exceptional strength, CSM gloves last significantly longer than NBR or neoprene, reducing replacement costs and minimizing workflow disruptions.
3.3 Particle-Free - Cleanroom Compliant
A key requirement in pharmaceutical environments is particle and contamination control. CSM gloves feature a stable, non-shedding structure that prevents particulate release even during rigorous tasks or sterilization cycles. This makes CSM ideal for:
- ISO Class 5-7
- EU-GMP Grade A/B within isolators
- Avoiding cross-contamination and protecting product integrity
This is a performance level that latex and many nitrile gloves often cannot achieve under high-pressure operations.
3.4 Easy to Sanitize - Sterilization Compatible
CSM gloves are compatible with multiple sterilization and disinfection methods, crucial for injectable drug and biologic production:
- UV sterilization
- Vaporized hydrogen peroxide (VHP)
- 70% IPA and common disinfectants
Importantly, CSM gloves do not discolor or become brittle after repeated sanitation cycles, maintaining their operational stability over time.
3.5 Ergonomic Design - Comfort for Prolonged Use
In addition to technical benefits, CSM offers superior user comfort compared to other thick and rigid materials:
- Flexible fingers and high elasticity enable precise manipulation in delicate operations
- Optimized surface friction - not too slick, not too rough
- Minimizes hand fatigue, unlike thick nitrile or neoprene gloves that may strain fingers and wrists during long sessions
These features reduce mechanical strain on technicians, particularly during 1-3 hour isolator shifts.
4. Quality Standards and Certifications for CSM Gloves
In pharmaceuticals, any equipment or material that contacts products indirectly must meet stringent safety, cleanliness, and biocompatibility standards. CSM gloves used in isolators must not only meet high-quality benchmarks but also have international and domestic certifications. Key standards include:
4.1 FDA 21 CFR 177.2600
This regulation evaluates rubber materials for indirect contact with pharmaceuticals and food. It is mandatory for gloves used in injectable drug and biologic manufacturing.
It defines:
- Suitable rubber types for pharma applications
- Limits on extractables from glove materials
- Safe additive content in rubber compounds
- Health and safety compliance for indirect contact
Benefits in GMP settings:
- Ensures material safety for product protection
- Supports equipment qualification (EU-GMP requirement)
- Facilitates regulatory audits by health authorities or global clients
- Minimizes risk during routine inspections
This standard is regarded as essential for sterile injectable drug production.
4.2 Cleanroom & GMP Compliance
In addition to FDA, CSM gloves must meet cleanroom and mechanical standards set by international frameworks:
EU-GMP / WHO-GMP:
- Gloves in Grade A/B must be particle-free
- Must not degrade when exposed to solvents
- Compatible with VHP, IPA, and UV sterilization
ISO 14644 (Cleanroom):
- Defines acceptable particle emission levels
- CSM meets ISO Class 5-7 for isolator use
EN 374 (Chemical Resistance):
- Measures glove resistance to acids, alkalis, and solvents
- CSM typically ranks at the highest levels
EN 388 (Mechanical Durability):
- Includes abrasion, tear, cut, and puncture resistance
- Premium CSM gloves achieve
These certifications form a robust compliance profile during audits.
4.3 Required Documentation for Use in Vietnam
Per current regulations, importing and using CSM gloves in pharmaceutical facilities requires:
CO (Certificate of Origin):
Verifies product origin, helps apply preferential tariffs with FORM E
CQ (Certificate of Quality):
Outlines technical specifications, standards, and batch details
No mandatory conformity certification:
CSM gloves are not general PPE or classified medical devices
No import license for medical devices required:
Not governed by Decree 98/2021/ND-CP for medical device registration
Accessory status under isolator systems:
- Considered a component like isolator ports or O-rings
- Avoids complex procedures per Vietnam Customs guidelines
5. Applications of CSM Gloves in Pharmaceutical Cleanrooms
CSM gloves are not just PPE-they are integral components of the isolator system in sterile pharmaceutical operations. Their high chemical resistance, mechanical durability, and tight sealing make them indispensable across various critical production stages, from API handling to injectable filling and microbiological testing.
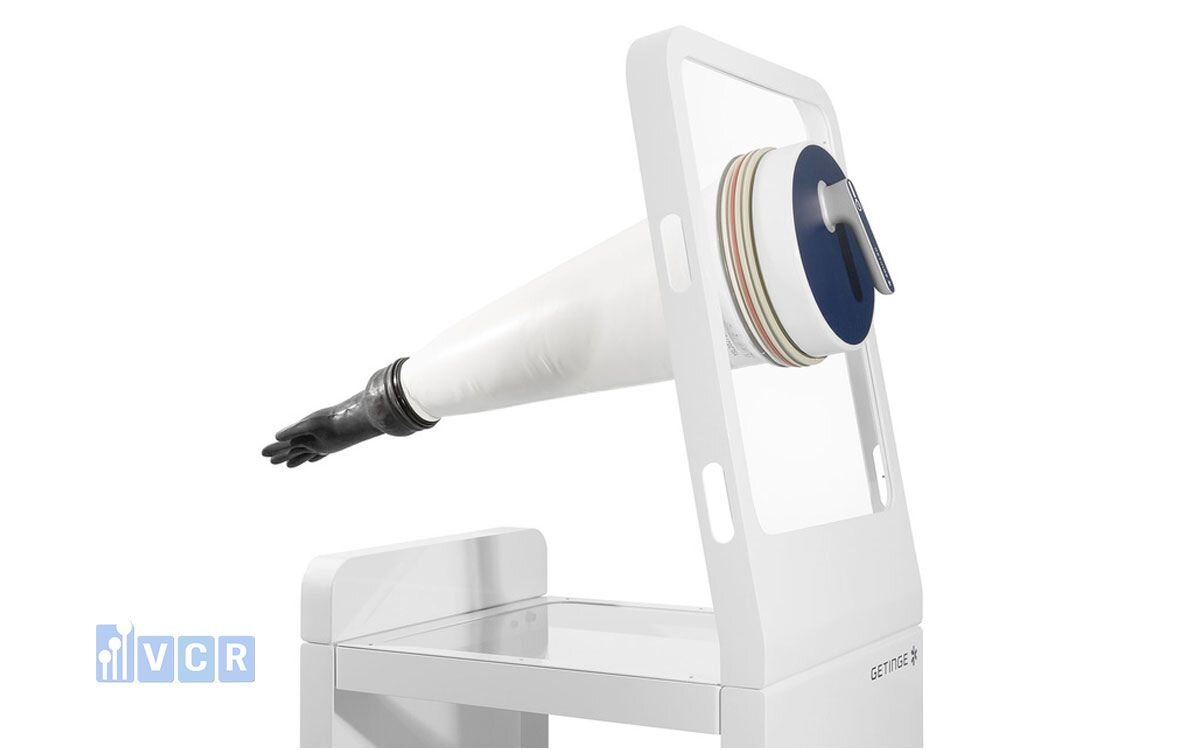
5.1 Isolator Operations
Isolators represent the most stringent Grade A environments for high-risk tasks. CSM gloves are essential for manipulating inside without compromising sterility.
Key uses include:
- Syringe filling: Requires the highest cleanliness level, gloves must be non-shedding and solvent-resistant
- Aseptic injectable manufacturing: Compounding, filtration, and filling demand ISO Class 5 compliance and reusability after sterilization
- Strong solvent exposure: CSM retains elasticity and durability against IPA, ethanol, acetone
- API/HPAPI handling: Requires puncture, tear, and chemical resistance
Toxic substance management: CSM ensures operator safety and prevents contamination
These properties make CSM the reference material for EU-GMP and PIC/S isolator gloves.
5.2 Microbiology & QC Laboratories
Microbiology and QC labs regularly use disinfectants and strong solvents like 70% IPA, ethanol, and industrial cleaners.
CSM gloves are ideal due to:
- Long-term chemical resistance
- Compatibility with biosafety cabinets
- Non-shedding under mechanical motion
- Maintains cleanliness when handling Petri dishes, culture media, or biological samples
They help prevent cross-contamination and ensure consistent testing results.
5.3 Compounding - Dosing - Filling Zones
In compounding and filling areas, technicians perform precise tasks with injectable drugs, eye drops, or sterile solutions.
CSM gloves support this with:
- Optimal surface friction for tool handling
- High elasticity for tactile sensitivity
- Solvent compatibility with pipettes, volumetric flasks, and automatic filling lines
5.4 R&D - Formulation - Vaccine Production
R&D centers and vaccine formulation labs handle high biological and chemical risks:
- Virus and biological sample handling
- Organic solvent extraction processes
- Cytotoxic drug manipulation
- Continuous UV or VHP sterilization
CSM's stability under multiple sterilization cycles ensures long-term operational safety.
5.5 Related Industries
Beyond pharma, CSM gloves are used in:
- Chemical Industry: Handling concentrated acids, alkalis, and solvents
- Electronics/Semiconductors: Anti-static, particle-free, and chemical-resistant
- Sterile/Low-heat food processing: FDA 21 CFR 177.2600 compliance allows indirect contact with food products
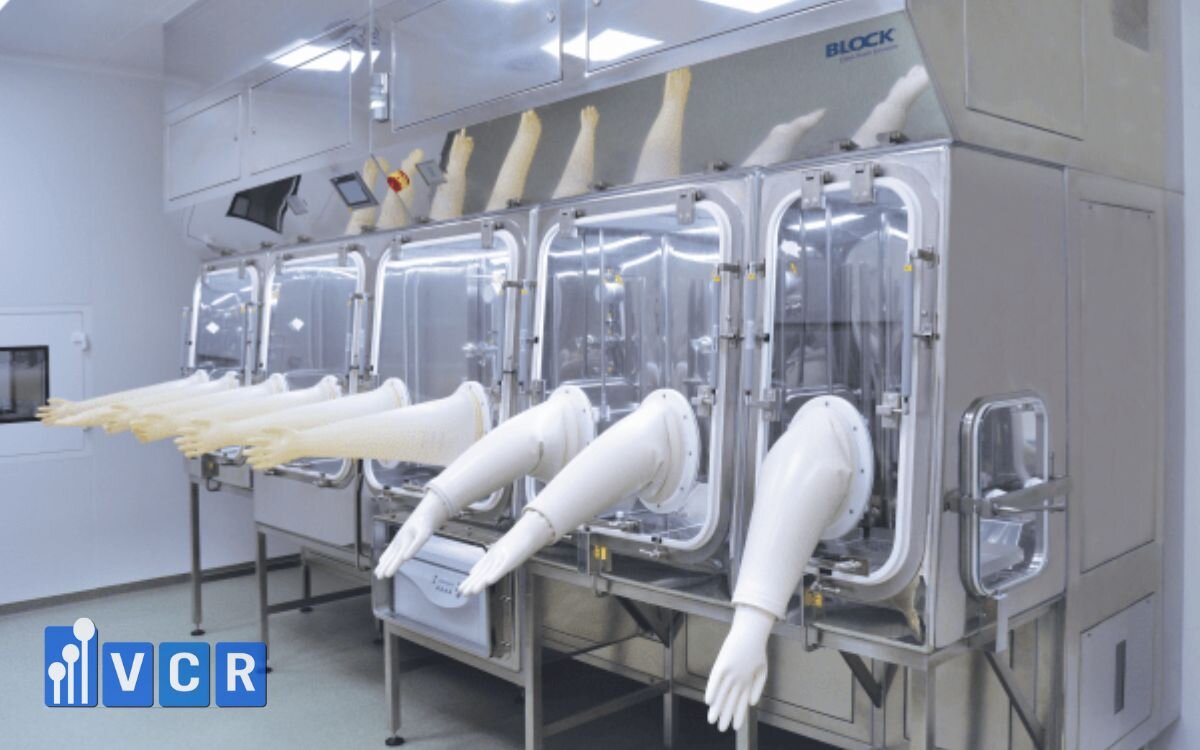
6. How to select CSM gloves correctly for each type of isolator
Choosing CSM gloves is not only about thickness or brand. To ensure safe operation and avoid affecting the aseptic production process, users need to determine the isolator port type, size, mounting style, and appropriate material thickness. The following detailed guide helps QA/QC, operations engineers and procurement teams make the correct choice.
6.1 Determine the port type and appropriate glove size
CSM gloves for isolators are designed with sizes similar to surgical gloves (from size 6 to size 10). This international sizing system ensures proper fit, snugness, and precise manipulation.
How to choose the appropriate size:
- Size 6-7: For users with smaller hands, typically female operators
- Size 7.5-8.5: Common size, suitable for most users
- Size 9-10: For users with larger hands or tasks requiring high comfort
Beyond hand size, the more important aspect is the diameter of the isolator port, which commonly comes in three sizes:
- 190 mm - Small isolator, minimal handling
- 230 mm - Common size, versatile
- 300 mm - Large isolator, injectable production areas or HPAPI handling
When selecting gloves, ensure:
- The glove diameter is compatible with the port flange
- The O‑ring or clamping ring system fully matches the equipment
- The glove length is sufficient to cover the entire arm during manipulation

6.2 Choose the appropriate thickness for each task
The thickness of CSM gloves determines durability, chemical resistance, and precision in use. Common thickness grades are:
- 0.4 mm - Fine manipulation: Suitable for laboratories, R&D, delicate operations
- 0.6 mm - Multipurpose: Most commonly used, balancing durability and natural feel; used in most compounding and filling zones
- 0.8 mm - Strong chemicals / HPAPI: For handling high‑concentration solvents or highly potent APIs; offers superior mechanical strength and integrity
Purchasers should consider the nature of the task when choosing thickness-avoiding selecting gloves that are too thick (which may cause hand fatigue) or too thin (which may lack sufficient durability).
6.3 Compatibility requirements with the isolator equipment
CSM gloves must be fully compatible with the isolator design to ensure containment and operator safety:
Mounting style:
- O‑ring (common)
- Mechanical clamping ring
- Rotating joint variant (depending on isolator brand)
Glove length: Typically 600-800 mm depending on the equipment and depth of the chamber:
- 600 mm: Smaller isolator
- 700 mm: Standard versatile size
- 800 mm: Used for HPAPI isolators or deep‑chamber isolators
Also check:
- Adhesion between the glove cuff and the port ring
- Whether the ring material is compatible with solvents
- Whether the glove is seamless or has weld seams
6.4 Maintenance and replacement considerations
To maintain optimal performance and safety, CSM gloves should be inspected and replaced on a regular schedule:
Replacement interval: 6-12 months depending on usage frequency, cleaning cycles and solvent exposure levels
Weekly inspections for:
- Cracks
- Signs of brittleness
- Reduced surface friction
- Reduced elasticity
Do not use sharp objects when operating, and avoid over‑drying the glove by excessive heat.
If any abnormal signs are detected, replace the glove immediately to prevent cross‑contamination or loss of isolator integrity.
7. Maintenance, Cleaning & GMP‑Compliant Use
While CSM gloves are premium materials, their lifespan can still be reduced if not handled and maintained properly. Within environments certified to EU‑GMP/WHO‑GMP, following correct procedures for usage, cleaning and inspection helps extend their service life and ensures the sterility and containment integrity of the isolator.
7.1 Donning, Doffing & Tear Inspection
Before installing CSM gloves on the isolator port, operators should perform checks and use correct technique to avoid damage:
- Pre‑installation inspection: Examine the entire glove surface for small tears, scratches, brittleness or thinned areas.
- Palm surface check: Any change in tactile friction may signal material ageing.
- Cuff inspection: Make sure the cuff isn’t deformed to ensure a tight seal with the isolator port.
- Avoid sharp or metal objects: Gloves must not contact metal edges, trays, utility knives or needles. Where sharp edges exist, protect with covers or accessories.
- Avoid overstretching: CSM gloves have good elasticity but excessive stretching may cause micro‑cracks. When installing on the port, apply even force-no twisting or jerking.
These steps help prevent glove breaches-a serious issue that can compromise isolator sealing and directly affect product quality.
7.2 Proper Cleaning & Disinfection
CSM gloves are designed for a variety of cleanroom‑friendly disinfection methods, however correct solutions and frequencies must be used.
- 70% IPA: Common in pharmaceuticals. Wipe gently and rotate the hand rather than apply heavy pressure.
- ClO₂ (Chlorine Dioxide): Suitable for periodic sterilisation. Unlike hypochlorite it does not embrittle the glove.
- VHP (H₂O₂ vapour): CSM is stable with VHP, showing no discoloration or bubbling. Often used in isolator sterilisation before production batches.
- UV exposure: Though CSM is UV resistant, avoid prolonged irradiation. Set a reasonable UV cycle to preserve glove longevity.
- GMP rule: Never clean gloves with coarse cloths or harsh scrub pads-these can erode the surface and cause hard‑to‑detect micro‑tears.
7.3 Common Mistakes That Reduce CSM Glove Lifespan
Many facilities replace their gloves too often due to misuse. Common faults include:
- Cleaning with overly aggressive solvents: Using high‑concentration acetone or toluene repeatedly reduces glove life. While CSM can tolerate exposure during operations, repeated wiping by such solvents degrades the material.
- Incorrect thickness selection: Using 0.4 mm gloves in heavy‑chemical zones reduces mechanical strength. Conversely, using 0.8 mm gloves for delicate tasks may force operators to apply excessive force, raising tear risk.
- Imprecise port fit: If the glove does not match the port in size (190/230/300 mm) or the sealing ring is mis‑matched, stress points form leading to embrittlement or tears over time.
8. CSM - The Gold Standard for Isolator Gloves in Modern Pharmaceutical Manufacture
In the context of the pharmaceutical industry increasingly adhering to strict standards such as EU‑GMP, WHO‑GMP and PIC/S, gloves are no longer just personal protective equipment-they become a vital component of the isolator system. The material CSM (Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene Rubber) has proven its superior position thanks to its strong chemical resistance, high mechanical durability, stability in sterile environments, and perfect compatibility with sterilisation processes such as IPA, UV or VHP.
At every stage of production-from compounding, filling, quality control, to handling API/HPAPI-CSM gloves help technicians operate safely while ensuring absolute cleanliness inside the isolator. Their non‑shedding nature, resistance to high‑intensity chemicals, good flexibility, and longer lifespan compared to conventional materials make CSM the first choice for pharmaceutical plants wanting to enhance stability and reduce production risk.
To select the correct CSM gloves, companies need to pay attention to port size, thickness, length, the O‑ring mounting system, quality certifications (FDA 21 CFR 177.2600, EN 374, EN 388, ISO 14644), together with CO/CQ documentation for import. Regular maintenance and inspection are also important in maintaining glove performance, minimising failure and extending service life.
In short, CSM gloves are not only a technically optimal solution but also a strategic choice that helps enterprises ensure production quality, elevate GMP compliance and reduce long‑term operating costs. They truly represent the “gold standard” for every isolator system in the pharmaceutical, biologics and modern cleanroom industries.
Reference & Contact - VCR
If your company is seeking international‑standard CSM gloves suitable for pharmaceutical isolators or sterile production areas, Cleanroom Equipment VCR is ready to supply:
- CSM gloves 404, 602, thickness 0.4‑0.8 mm
- CSM gloves 600‑800 mm long, compatible with port sizes 190 / 230 / 300 mm
- Seamless product lines (no weld seams) compliant with EU‑GMP
- Full CO, CQ documentation - technical consultancy - support for port installation
- Quick quotation in 30 minutes
Hotline: 090.123.9008
Email: [email protected]
Website: https://vietnamcleanroom.com/
Diep VCR




















