What is an electrostatic dust collector?
What is an electrostatic dust collector? What is the structure and operating principle of an electrostatic dust filter? Application of electrostatic dust collector in industrial environments
- What is an electrostatic filtration?
- Structure of electrostatic dust filter
- Operating principle of electrostatic dust filtration
- Electrostatic dust filter collector Performance
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Electrostatic Dust Collectors
- Types of Electrostatic Dust Collectors
- Electrostatic Dust Filtration Systems Applications
Industry is an indispensable part of our lives, but it also causes serious impacts on the environment and the health of workers. However, in the current era of technological advancements, many effective solutions have been developed to address these issues.
In this article, VCR introduces the electrostatic dust filtration, a widely adopted solution for mitigating industrial dust-related problems.
What is an electrostatic filtration?
The electrostatic dust filtration is a filtration system used to remove fine particles such as smoke and fine dust from the airflow. It is a system commonly used to control air pollution in various industries.
In 1907, chemistry professor Frederick Gardner Cottrell patented the first electrostatic dust extraction system used to collect sulfuric acid mist and lead oxide fumes emitted from various smelting and acid formation activities.
Today, this system is considered an optimal solution for purifying exhaust gases in the manufacturing industry, making it a popular choice for many businesses.
Structure of electrostatic dust filter
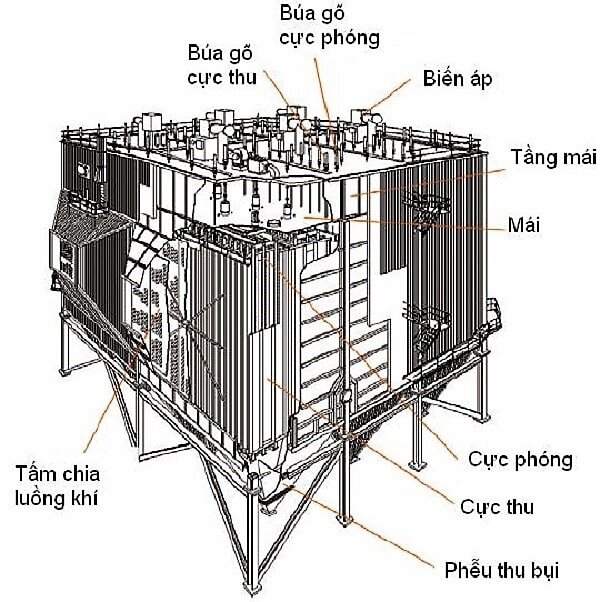
Electrostatic dust collectors are designed in a circular tower arranged in a honeycomb or rectangular box structure. Inside the tower, at the filter chamber, there are parallel polar plates or discharge wires.
The structure of this electrostatic dust collector includes two main components:
- Mechanical parts: filter chamber shell, electrode spikes, and dust vibration motor.
- Electrical and control components: high-voltage control cabinet and rectifier bridge.
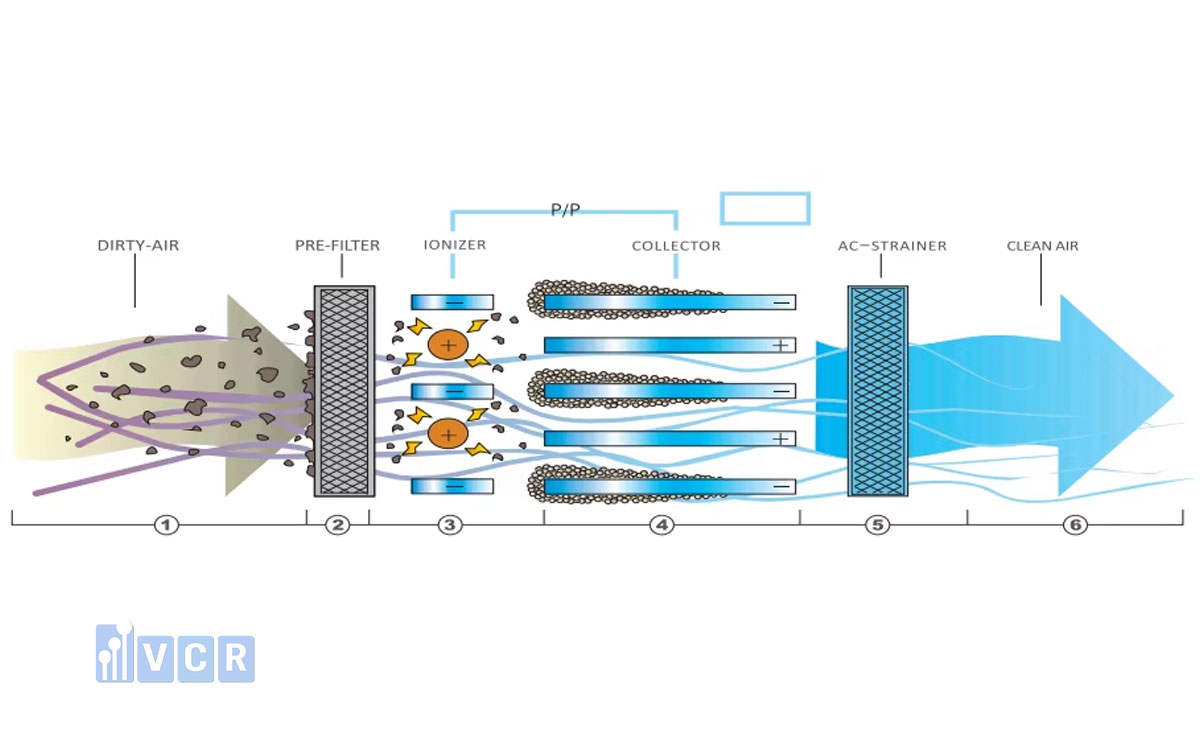
Operating principle of electrostatic dust filtration
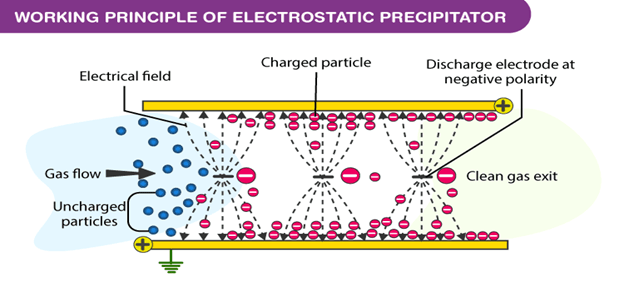
The operating principle of the electrostatic dust collector involves two sets of electrodes: positive and negative. The negative electrodes are in the form of discharge wires, while the positive electrodes are plates. These electrodes are placed vertically and alternated with each other.
A high-voltage DC source connects the negative electrodes (cathode) and the positive electrodes (anode). Ionization occurs between the negative and positive electrodes due to the high voltage gradient maintained between them.
The medium used between the two electrodes is air. A corona discharge is generated around the discharge wires due to the high negative charge. Free electrons produced during ionization interact with dust particles in the gas, charging them negatively. These negatively charged particles are attracted to the positive electrodes, where they accumulate and are periodically removed by mechanical shaking or rapping.
The entire system is enclosed in a metal box with an inlet for exhaust gas and an outlet for filtered gas. The exhaust gas is significantly cleaner after passing through the electrostatic dust collector and is discharged into the atmosphere through the chimney.
Electrostatic dust filter collector Performance
The performance of an electrostatic dust collector depends on various environmental and operational factors. Key factors influencing system efficiency include:
- The size and density of dust particles in the airư
- Airflow velocity and its uniform distribution within the electric field area
- Design and material properties of the electrodes
- Electrical characteristics and stability of the devices controlling the electric field
Additionally, the system can automatically adjust the high voltage in the filter chamber based on dust concentration and airflow characteristics to achieve optimal dust filtration efficiency. Under ideal operating conditions, this system can achieve a dust filtration efficiency of over 98%.
Dust accumulated on the electrode plates can be removed by either washing with water or mechanical shaking.
The performance of the electrostatic dust collector can be calculated using the following efficiency formula, which considers various operational parameters:
= 1-e(-WA/Q)
In which:
- e is the efficiency of collecting fractions
- W is the final drift velocity in ms -1
- A is the total collection area in m 2
- Q is the volumetric air flow rate in m s -1
Advantages and Disadvantages of Electrostatic Dust Collectors
Electrostatic dust collectors have distinct advantages and disadvantages as an environmental treatment solution, including:
Advantages:
- High durability and reliability of the electrostatic dust collector (ESP).
- Efficiently collects both dry and wet impurities, depending on the design.
- Low operating costs compared to other filtration systems.
- High collection efficiency, even for very small particles.
- Capable of handling large volumes of gas and heavy dust loads at low pressure.
Disadvantages:
- Ineffective at removing certain gaseous pollutants or volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- Requires significant installation space due to its large size and complex structure.
- High initial investment cost.
- Limited adaptability to sudden changes in dust load, temperature, or humidity levels.
Types of Electrostatic Dust Collectors
There are various types of electrostatic dust collectors designed for different industrial applications. Below are some common types available on the market today:
Plate Dust Filter
This is a basic type of dust collector consisting of vertical thin wires and large flat metal plates arranged vertically, spaced 1 cm to 18 cm apart. The airflow passes horizontally through the wires and then between the plates. A negative voltage applied between the wires and plates ionizes the dust particles, which are attracted to the grounded plates by electrostatic force. Collected particles are periodically removed from the plates using mechanical rapping.
Dry Electrostatic Precipitator
Used to collect pollutants like dust and cement in a dry state. It includes electrodes that ionize the particles in the gas flow and a hopper to store and extract collected particles. Dust is removed from the plates by vibrating or rapping the electrodes.
Wet Electrostatic Filter
This type is used for fine particulate removal, such as plastic particles, oil mist, tar, and wet paint overspray. Collection surfaces are continuously sprayed with water, which washes away the particles into a sludge collection system. Wet filters are more effective than dry systems for certain sticky or liquid-bound particulates.
Tubular Dust Filter
This filter consists of cylindrical tubes with electrodes running along their axes, arranged parallel to each other. The tubes may form circular, square, or hexagonal honeycomb structures, with air flowing vertically through them. Tubular filters are ideal for removing sticky or tar-like particles and are commonly used in industrial applications requiring high precision.
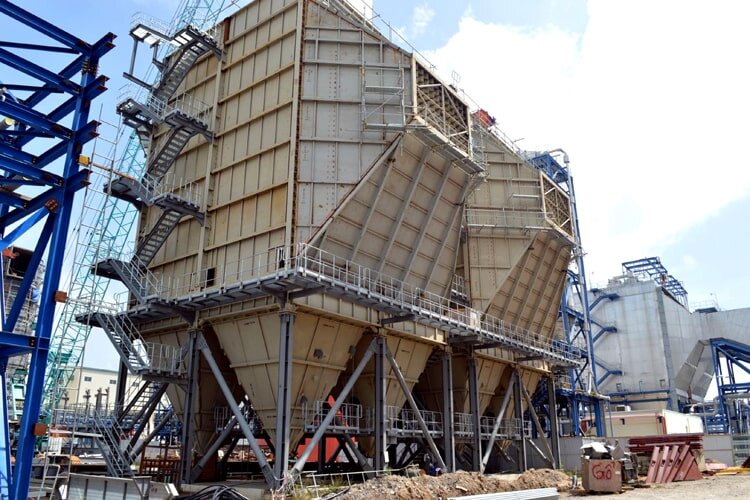
Electrostatic Dust Filtration Systems Applications
Thanks to their excellent dust filtration features and performance, electrostatic dust filtration systems are widely applied in various fields. Below are some notable applications:
ESP Plates in Ship Engine Rooms
ESP plates are used in ship engine rooms to capture explosive oil mist produced by gearboxes. The collected oil can be reused in the gear lubrication system, enhancing efficiency and reducing waste.
Dry ESP in Thermal Power Plants
Dry ESP systems are employed in thermal power plants to remove dust and particulate matter from flue gases, ensuring cleaner emissions and compliance with environmental regulations.

Medical Field Applications
ESP systems are applied in medical facilities to capture airborne bacteria and fungi, significantly improving air quality in sensitive environments such as operating rooms and laboratories.
Zirconium Sand Processing
Electrostatic dust filters are utilized in zirconium sand processing to separate rutile from other materials, ensuring higher purity in industrial production processes.
Metallurgical Industry
Electrostatic dust filtration systems are used in the metallurgical industry to remove particulate matter and clean gases produced during smelting and metal refining processes.